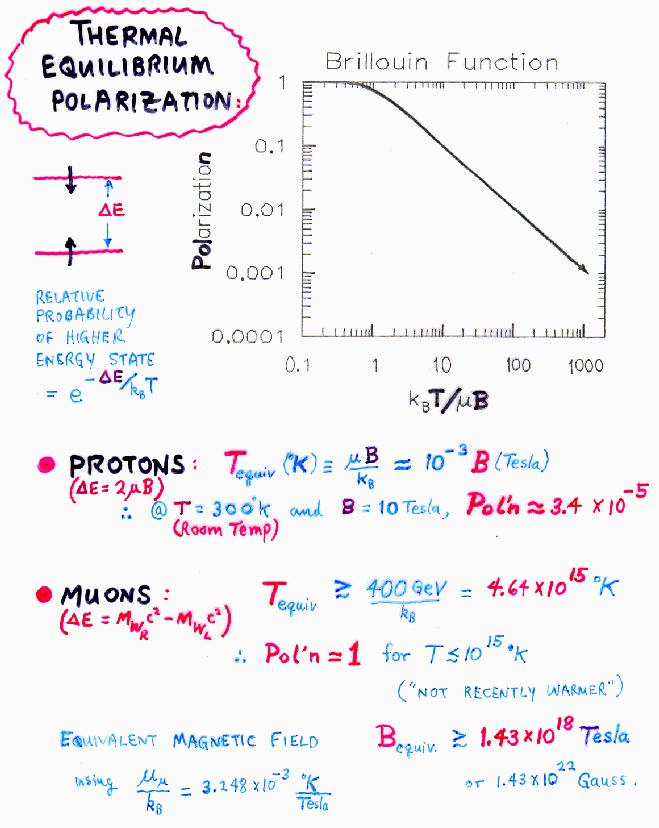
Spin Polarization
In proton NMR (for example) the proton spins are polarized
in thermal equilibrium by application of a strong magnetic
field which splits the energy of spin-up and spin-down protons
by the Zeeman energy and thus favours the population of the
spin-up state - but not by much!
By contrast, the muon's polarization is a consequence of
the mass difference between the left-handed W boson
and its hypothetical right-handed partner - a difference of
at least 400 GeV!
It is amusing to compare the temperatures or magnetic fields
that would be required to achieve a similar polarization of
protons....
Jess H. Brewer
Last modified: Fri Nov 28 16:16:05 EST

